TSS assembly pipeline for Rm_EPDnew_001
Introduction
This document provides a technical description of the transcription start site assembly pipeline that was used to generate the EPDnew version 001 for M. mulatta.Source Data
Promoter collection:
| Name | Genome Assembly | Promoters | Genes | PMID | Access data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSEMBL92 genes | Nov 2015 BCM Mmul_8.0.1/rheMac8 | 36903 | 20593 | 29092050 | SOURCE | DOC | DATA |
Experimental data:
| Name | Type | Samples | Tags | PMID | Access data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| francescatto17 | CAGE | 15 | 217,883,048 | 29087374 | SOURCE | DOC | DATA |
Assembly pipeline overview
|
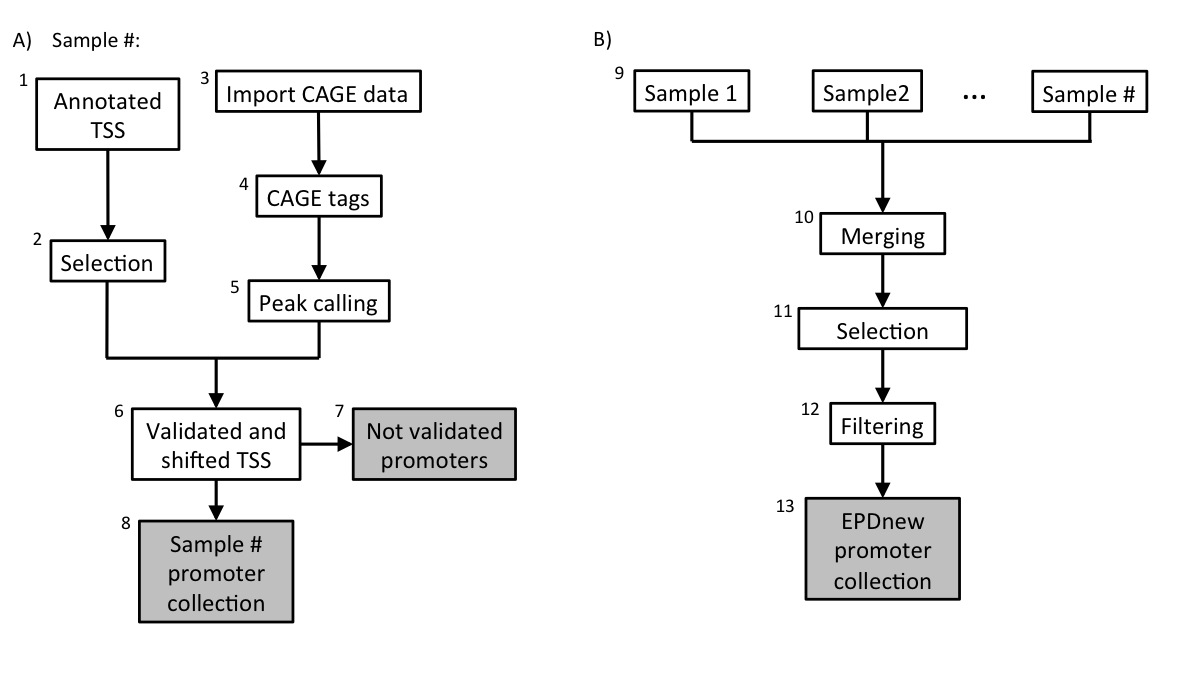
Description of procedures and intermediate data files
1. Ensembl Download
Data was downloaded from ENSEMBL in July 2018. Transcripts have been filtered according to the following rules:- Transcripts of protein coding genes only
- Transcripts on full chromosomes
- Genes must be annotated [Gene Name present]
- Genes' and transcripts' status known
2. Ensembl TSS collection
The Ensembl TSS collection is stored as a tab-deliminated text file conforming to the SGA format under the name:-
Rm_ensembl92_tss_rheMac8.sga
- NCBI/RefSeq chromosome id
- "TSS"
- position
- strand ("+" or "-")
- "1"
- ENSEMBLGeneID .. geneName
3. Data import from FANTOM5
BAM files for high quality CAGE samples (hCAGE) were downloaded from FANTOM5 ftp site (link above). Files were then converted into SGA format using in-house software. There are a total number of 15 samples in this collection. Individual SGA files can be downloaded from our ftp website (link above).5. mRNA 5' tags peak calling
For each individual sample, peak calling for the merged file has been carried out using ChIP-Peak on-line tool with the following parameters:- window width = 1
- vicinity range = 200
- peak refine = Y
- count cutoff = 9999999
- threshold = 5
6. TSS validation and shifting
Each sample in the collection (mRNA peaks and Ensembl TSS) was then separately processed in a pipeline aiming at validating transcription start sites with mRNA peaks. An Ensembl TSS was experimentally confirmed if an mRNA peak lied in a window of 200 bp around it or if it mapped in the 5' UTR region. The validated TSS was then shifted to the nearest base with the highest tag density.8. Promoter collection for each sample
Each sample in the dataset was used to generate a separate promoter collection. Potentially, the same transcript could be validated by multiple samples and it could have different start sites in different samples. To avoid redundancy, the individual collections were used as input for an additional step in the analysis (assembly pipeline part B).9. Merging collections and second TSS selection
The 15 promoter collections were merged into a unique file and further analyzed. The promoter of a transcript was kept in the list only if validated by at least two samples. Transcripts validated by multiple samples could potentially have the TSS set on a broader region rather than a single position. To avoid such inconsistency, we selected for each transcript the position that was validated by the largest number of samples as the true TSS.10. Filtering
TSSs that mapped close to other TSSs that belonged to the same gene (500 bp window) were merged into a unique promoter following the same rule: the promoter that was validated by the highest number of samples was kept.10. Final EPDnew collection
The 9575 experimentally validated promoters were stored in the EPDnew database, which can be downloaded from our ftp site. Scientists are welcome to use our other tools ChIP-Seq (for correlation analysis) and SSA (for motif analysis around promoters) to analyze the EPDnew database.Last update October 2019