TSS assembly pipeline for Sp_EPDnew_002
Introduction
This document provides a technical description of the transcription start site assembly pipeline that was used to generate EPDnew version 002 for S. pombe.
Source Data
Promoter collection:
| Name | Genome Assembly | Promoters | Genes | PMID | Access data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RefSeq Genes | Aug 2015 ASM294v2/spo2 | 5128 | 5128 | 22121212 | SOURCE | DOC | DATA |
Experimental data:
| Name | Type | Samples | Tags | PMID | Access data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al., 2015 | DeepCAGE | 1 | 17,279,045 | 25747261 | SOURCE | DOC | DATA |
| Thodberg et al. 2018 | CAGE | 15 | 276,570,639 | doi:281642 | SOURCE | DOC | DATA |
Assembly pipeline overview
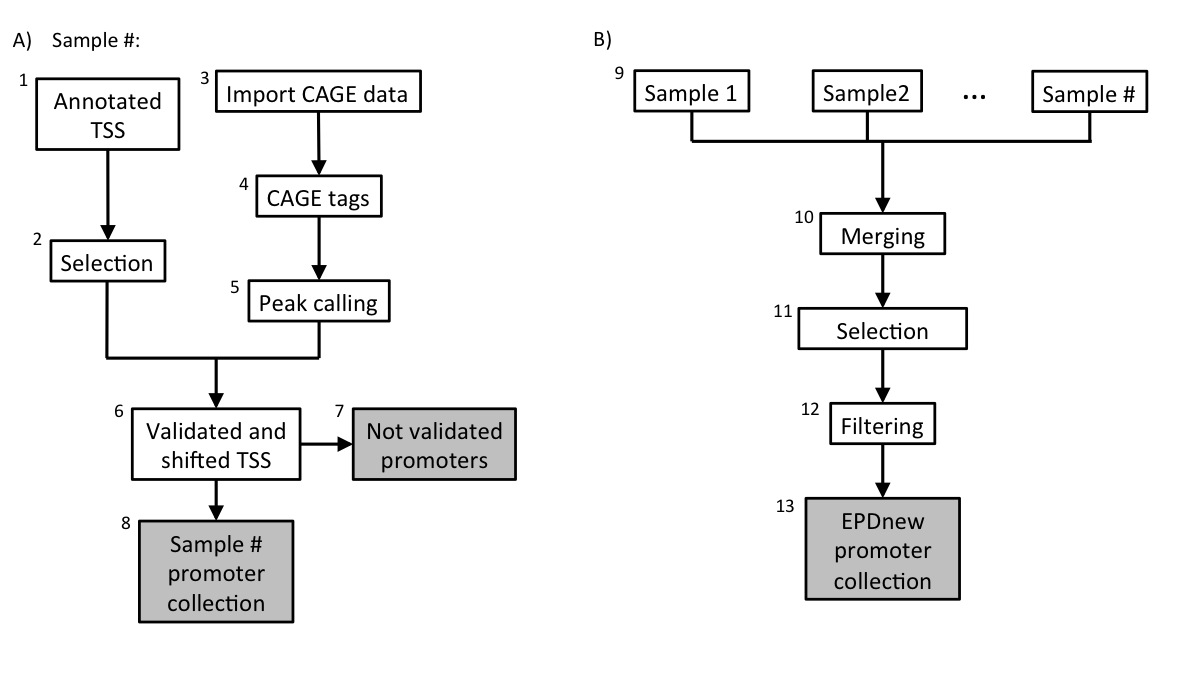
|
Description of procedures and intermediate data files
1. Download annotated TSS
Data was downloaded from NCBI RefSeq database, the 02-02-2015. Transcripts have been filtered for protein coding gene only, removing pseudogenes from the list.Gene names were taken from the field "Locus ID". Since the EPD format doesn't allow gene names longer than 18 characters, we checked whether the names respected this limitation.
A total number of 5128 promoters were selected.
2. SGD TSS collection
The RefSeq TSS collection is stored as a tab-delimited text file conforming to the SGA format under the name:-
spo2TssFromRefSeq.sga
- NCBI/RefSeq chromosome id
- "TSS"
- position
- strand ("+" or "-")
- "1"
- gene name
3. Import CAGE data
Data was imported from ArrayExpress as FASTQ file format. Raw sequence files were mapped to spo2 genome using Bowtie (trimming 1bp from the 5-end). The resulting BAM files were converted to SGA file format using ChIP-Convert.A step-by-step guide on how to import, map and convert these samples can be found here
5. mRNA 5' tags peak calling
For each individual sample (3), peak calling for the merged file has been carried out using ChIP-Peak on-line tool with the following parameters:- Window width = 200
- Vicinity range = 200
- Peak refine = Y
- Count cutoff = 9999999
- Threshold = 5
6. TSS validation and shifting
Each sample in the collection (mRNA peaks and UCSC TSS) was then separately processed in a pipeline aiming at validating transcription start sites with mRNA peaks. A UCSC TSS was experimentally confirmed if an mRNA peak lied in a window of 500 bp around it. The validated TSS was then shifted to the nearest base with the higher tag density.7. UCSC not-validated TSS
The total number (summing up all samples) of non experimentally validated TSS was around 2000.8. Promoter collection for each sample
Each sample in the dataset was used to generate a separate promoter collection. Potentially, the same transcript could be validated by multiple samples and it could have different start sites in different samples. To avoid redundancy, the individual collections were used as input for an additional step in the analysis (Assembly pipeline part B).9. Merging collections and second TSS selection
The sample-specific promoter collections were merged into a unique file and further analyzed. Transcripts validated by multiple samples could potentially have the TSS set on a broader region rather than a single position. To avoid such inconsistency, for each transcript we selected the position that was validated by the larger number of samples as the true TSS.10. Filtering
Transcription Start Sites that mapped closed to other TSS that belonged to the same gene (500 bp window) were merged into a unique promoter following the same rule: the promoter that was validated by the higher number of samples was kept.10. Final EPDnew collection
The 4802 experimentally validated promoters were stored in the EPDnew database, which can be downloaded from our ftp site. Scientists are welcome to use our other tools ChIP-Seq (for correlation analysis) and SSA (for motif analysis around promoters) to analyze the EPDnew database.Last update October 2019