A set of fixed-length DNA sequences aligned with
respect to a functional site, e.g. a transcription start
site, is scanned in a sliding window in order to determine
the occurrence frequency of a particular sequence motif
(signal) defined by a particular signal. Multiple sets
can be processed at the same time. The output is a graph
showing the occurrence frequency of the signal as a
function of its position relative to the functional sites.
A detailed description of the method can be found
here
MEME Motif Format
The motif library provided by SSA have been originally downloaded from The MEME Suite website. Motifs have then undergone a reformatting process (for more details, please read here).
Matrices from MEME are provided in two formats:
- as letter-probability matrices;
- as integer log-odds weight matrices.
The conversion of base counts into weights is given by the formula shown here:
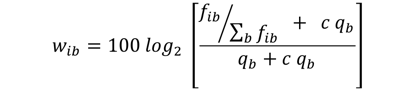 (1)
(1)
where fib is the relative frequency of base b at PWM position i, qb is the background frequency of base b, and c is the fraction of pseudo-counts added to the observed base frequencies.
Unless specified otherwise, background letter frequencies are those from a uniform background (A 0.25000 C 0.25000 G 0.25000 T 0.25000).
Weights are rounded to nearest integers to allow for efficient computation of the probability distribution for scores expected from random sequences.
For more details, visit the MEME website or our PWMLib site .