spEPDnew, the Schizosaccharomyces pombe (fission yeast) curated promoter database
|
|
Promoter Selection and Analysis tools
Various tools allow you to analyse promoters from EPD and/or to select subsets of promoters. In order to analyze the complete EPD promoter set, go directly to one of the analysis pages. If you prefer to first select a subset of promoters, go to one of the selection pages. From the output of the selection pages you can then directly navigate to one of the analyses pages, or you can continue with another selection page to refine your promoter selection.
Selection tools
|
Analysis tools
|
| How-To Documentation: OProf, FindM and ChIP-Cor. |
Database quality control
Core promoter elements' enrichment
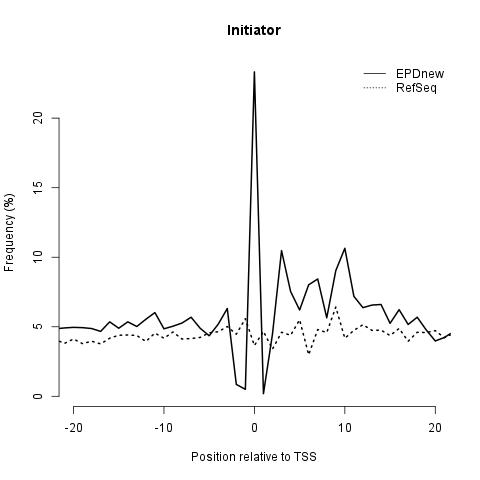
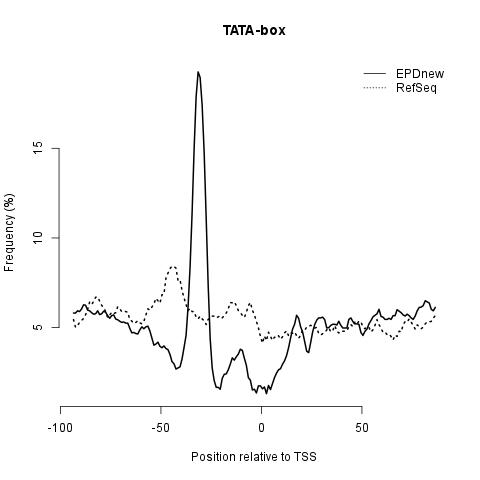
Core promoter element analysis is performed in order to investigate the quality of the promoter collection. It leverages the preferential occurrence of certain DNA motifs at characteristic distances from the TSS. For instance, TATA boxes occur in a narrow region centered about 28 bp upstream of the TSS, whereas the CCAAT box occurs in a much wider area, with a maximal frequency at position -80. Based on these observations, a high-quality promoter collection is expected to show high peaks for both motifs. In addition, a narrow TATA box peak at -28 would indicate precise TSS mapping. This analysis has been performed using OProf. EPD users are encouraged to repeat this analysis and to perform others in order to check the quality of the promoter list.
TATA-box: this core promoter element is normally found 28 bp upstream the transcription start site. The following plot shows that EPDnew promoter collection has a more focused TATA-box distribution compared to RefSeq annotation suggesting a precise TSS mapping in EPDnew.
Initiator: it is found at the TSS and shows a great enrichment in EPDnew compared to RefSeq promoter collection.